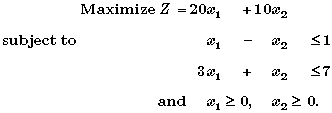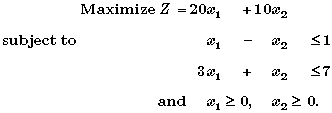| Using money units of thousands of dollars and time
units of hours, the data for Leo's problem can be summarized as
follows. |
 |
| Since Leo must decide how many shares of each venture to
take, the
decision variables are |
| 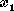 = number of shares of Venture 1,
= number of shares of Venture 1,
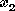 = number of shares of Venture 2.
= number of shares of Venture 2. |
| He wants to maximize his savings, so the value of the objective
function is |
| 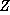 = number of money units (thousands of dollars) added to savings.
= number of money units (thousands of dollars) added to savings. |
| The linear programming model for Leo's problem now can
be formulated from the data in the table as follows. |
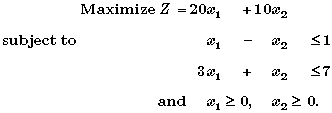 |