Example: The U.S. market for baby blouses (Q=millions)
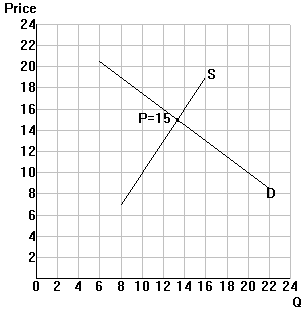
|
Wednesday, March 07, 2012 |
Trade policy analysis 1: tariffs
Example: The U.S. market for baby blouses (Q=millions)
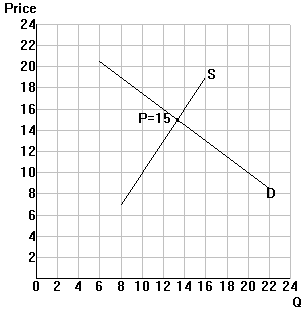
A. Free trade: The diagram above
illustrates the situation faced by the U.S. before it trades.
Step 1: Suppose Pf = $10. In the diagram, plot Pf and label the free-trade
equilibrium quantities.
Step 2: Fill in the free-trade values in Table
1.
B. Tariff: the U.S. imposes a $3 tariff on imported blouses.
B1. Price and quantity effects
Step 1: In the diagram, shift Pf up by the amount of the tariff (label your new
curve Pf+tar);
Step 2: Label the new domestic price and
equilibrium with the tariff.
Step 3: Fill in the tariff values in Table 1.
| Table 1 | ||
| Situation in the U.S.: | Free trade | $3 Tariff |
| Price | ||
| Quantity produced | ||
| Quantity consumed | ||
| Quantity imported | ||
B2. National welfare effects: Comparing the tariff to free
trade:
Step 1: In the diagram, indicate the change in consumer surplus (\\\), producer surplus
(///), and government revenue (|||), and indicate the net change in U.S. welfare.
Step 2: Complete Table 2.
| Table 2: tariff versus free trade | |||
| Gain or loss? | Area in graph | Amount | |
| Change in consumer surplus | loss | ||
| Change in producer surplus | |||
| Change in government revenue | |||
| Change in national welfare | |||