|
Friday, February 22, 2013 |
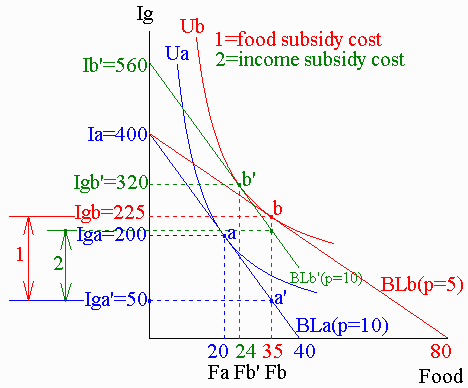
Contrasting price and income subsidies
Consider the Smiths, a low-income family which has a $400 income to spend on food (F) [market price = Pmkt = $10 per meal], with the rest spent on other goods (Io).
Option 1: the government offers
a 50% food price subsidy, so the Smiths pay a subsidized price = Psub = $5 per meal
Option 2: the government offers the
Smiths a utility-equivalent income subsidy.

| Consumption point | Money income | Pfood | Qfood | TEfood | Ig ($) | Cost to government | ||
| (0) | No subsidy | a | --- | |||||
| (1) | Food price subsidy | |||||||
| (2) | Utility-equivalent income subsidy |