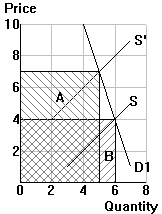
P2=7, Q2=5: TE2 = ______
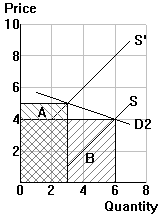
P2=5, Q2=3: TE2 = ______
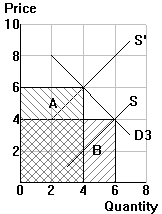
P2=6, Q2=4: TE2 = ______
Arc price elasticity of demand
Own-price elasticity of demand: general formula: e = %DQd/%DP. (Note: by the law of demand Qd and P always move in the opposite directions, so e is always negative. In practice, most economists drop the sign and focus only on the size. We'll do that.)
Q2 - Q1
------------
%DQd
(1/2)(Q2+Q1)
Arc method: e = ----- = --------------
%DP
P2 - P1
------------
(1/2)(P2+P1)
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
 |
 |
 |
| P1=4, Q1=6: TE1 = ______ P2=7, Q2=5: TE2 = ______ |
P1=4, Q1=6: TE1 = ______ P2=5, Q2=3: TE2 = ______ |
P1=4, Q1=6: TE1 = ______ P2=6, Q2=4: TE2 = ______ |
| e = ______ | e = ______ | e = ______ |
| Classification of demand elasticity (elastic, unit elastic, inelastic): | ||
| _______________ | _______________ | _______________ |
| The rules of elasticity (allow you to predict how price and total expenditure are related): | ||
| |
|
|
Test your understanding:
1. True or false? If quantity demanded falls when the price rises, then
demand must be elastic.
Answer: ___
2. If price rises by 30% and total revenue rises by only 10% then
demand is
a. elastic. b.
inelastic. c. unit elastic.
Answer: ___