Price ceiling
Price floor

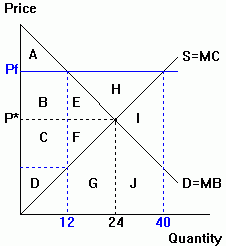
The economic effects of price controls
Price ceiling |
Price floor |
 |
 |
Complete the price ceiling information in the table below. The price floor information has been provided as an example:
| Price ceiling | Price floor | |||||
| Free market | Price ceiling | Change | Free market | Price floor | Change | |
| P* | Pc | --- | price (P) | P* | Pf | --- |
| 24 | --- | quantity demanded (Qd) | 24 | --- | ||
| 24 | --- | quantity supplied (Qs) | 24 | --- | ||
| --- | --- | suprlus/shortage | --- | --- | ||
| ABE | consumer surplus (CS) | ABE | ||||
| CDF | producer surplus (PS) | CDF | ||||
| ABCDEF | total social welfare (SW) | ABCDEF |
* |
|||
Price controls have a variety of predicted effects:
1. Quantity shortages (with price ceilings) and surpluses (with price floors)
2. Welfare losses
3. Wealth transfers
4. "Non-price" rationing
5. Cheating and evasion
6. Product quality adjustments
*Note regarding the estimated welfare loss of a price floor: This loss presumes that steps are taken to restrict the final production of suppliers to the quantity that buyers will purchase. Failure to accomplish that will result in a different and larger welfare loss due to overproduction that cannot be sold.