| Summary of the three examples: |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
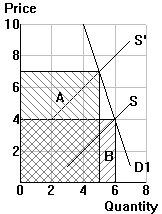
(1) Inelastic demand |
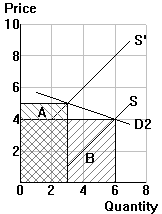
(2) Elastic demand |
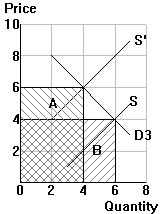
(3) Unit elastic demand |
| |
|
| 1. |
Quantity demanded (Qd) follows the law of
demand: demand curves always slope down, so a higher price (P) results in a lower
quantity demanded (Qd). This holds in all three cases |
| |
|
| 2. |
Total expenditure (TE) follows the rules of
elasticity (formula: e = %DQd / %DP):
|
 |
| (1) |
e < 1 |
=> demand is inelastic |
=> the price effect (A) dominates
=> price and total expenditure move in the same direction |
| (2) |
e > 1 |
=> demand is elastic |
=> the quantity effect (B) dominates
=> price and total expenditure move in opposite directions |
| (3) |
e = 1 |
=> demand is unit elastic |
=> the price (A) and quantity (B) effects offset each other
=> total expenditure remains constant when price changes |
|
| |
|


