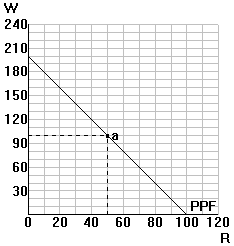

Ricardian trade model geometry
Home country production and pretrade situation:
| Home country production information: | Output per labor hour | |
| Razors (R) | Wigs (W) | |
| 1 | 2 | |
| => opportunity cost of each razor = 2
wigs => at home, before trade (autarky): PR = 2PW => PR / PW = 2 |
||
Suppose Home has 100 total labor hours available and divides its labor equally between R and W before trade => production and consumption = 50 razors and 100 wigs.
Free trade:
Suppose that with free trade, Home exports 20%
of the total production of its export product.
Do the following for each case depicted in the table below:
Step 1: Draw Home's
free trade budget line through its initial production point; label it BLfa.
Step 2: Draw an arrow
(and label it '1') indicating which direction Home should move to reach
its highest attainable free-trade budget line and label Home's final free-trade production
point b. This illustrates Home's specialization.
Step 3: Draw Home's
free trade budget line through point b; label it BLfb.
Step 4: Draw an arrow
(and label it '2') along BLfb illustrating Home's
exchange (trade), and label its final consumption point c, assuming that Home exports 20% of the
total production of its export product.
Step 5: Complete the table
of values for Home's free-trade production, trade and
consumption.
| Case 1: On the world market, PR/PW = 8 | Case 2: On the world market, PR/PW = 1/2 | ||||
 |
 |
||||
| R | W | R | W | ||
| Production | ______ | ______ | Production | ______ | ______ |
| Trade | ______ | ______ | Trade | ______ | ______ |
| Consumption | ______ | ______ | Consumption | ______ | ______ |
| Cons. change vs. autarky | ______ | ______ | Cons. change vs. autarky | ______ | ______ |
Conclusion: Trade according to comparative advantage makes a country better off because it allows the country to consume more than it can produce itself. (The country can consume outside its PPC.)