| Consider point a, the initial distribution of (LT and KT). | 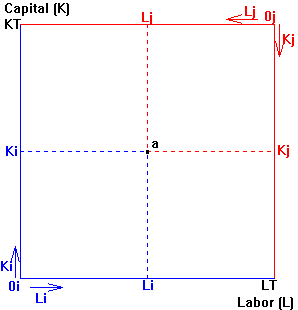 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | Use the following information to compute the MRTS for firms i and j: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Which firm has the greater productivity of labor
compared to capital?
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | What direction of trade will make both firms i
and j better off?
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Diagram isoquants which reflect the situation faced by these two firms at point a. Label them Qai and Qaj. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Now suppose that the two firms exchange 1L for 8K. Complete the following table: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Indicate in your diagram the direction the firms move from point a. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7. | a. | Diagram the highest attainable output for firm i if firm j produces Qaj. Label your new isoquant Qbi. Which output is higher, Qai or Qbi? ______ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| b. | Diagram the highest attainable output for firm j if firm i produces Qai. Label your new isoquant Qbj. Which output is higher, Qaj or Qbj? ______ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8. | Draw a contract curve (CC) which includes the two production points you illustrated in part 8. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. | The portion of a contract curve which can be reached via voluntary exchange from a given initial endowment is known as the "core" of the contract curve. Indicate the core determined by point a. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||