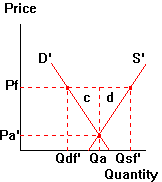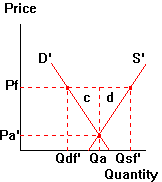Supply and Demand Geometry for International Trade
Depicting the Gains from Trade
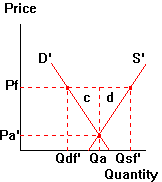 West market
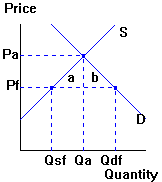
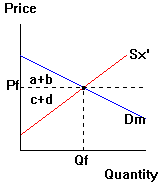
Trade market
East market
West market
Trade market
East market
Production adjustments lead to specialization
gains (these are sometimes referred to as production gains):
--An exporter increases production. The country
gains by selling the extra ouput on the world market for more than the
value of the resources used to produce it.
--An importer replaces some domestic production
with imports. The country gains by spending less on the replacement imports
than it saves by freeing up domestic resources.
In the diagram above: the exporter's specialization
gains = ______
the importer's specialization gains = ______
Consumption adjustments lead to exchange
gains (these are sometimes referred to as consumption gains):
--An exporter diverts some domestic consumption
to exports. The country gains by selling the diverted units on the world
market for more than their value to domestic consumers.
--An importer increases consumption with imports.
The country gains by acquiring extra units that consumers value more highly
than the price they pay.
In the diagram above: the exporter's exchange gains
= ______
the importer's exchange gains = ______
Specialization and exchange gains combine to yield
a country's overall gains from trade. Each country's gains from
trade show up in the trade market diagram.
In the diagram above: the exporter's gains from
trade = ______
the importer's gains from trade = ______