Figure 5.15 and 5.21
5.15 Transmitter actions at G-protein-coupled receptors. The binding of neurotransmitter to the receptor leads to the activation of G-proteins. Activated G-proteins activate effector proteins, which may be (a) ion channels or (b) enzymes that generate intracellular second messengers.
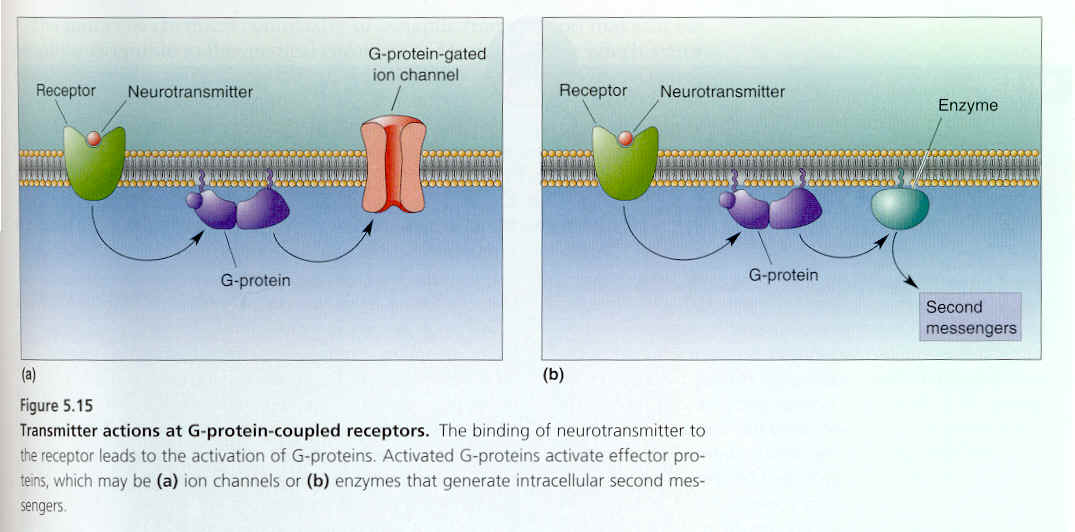
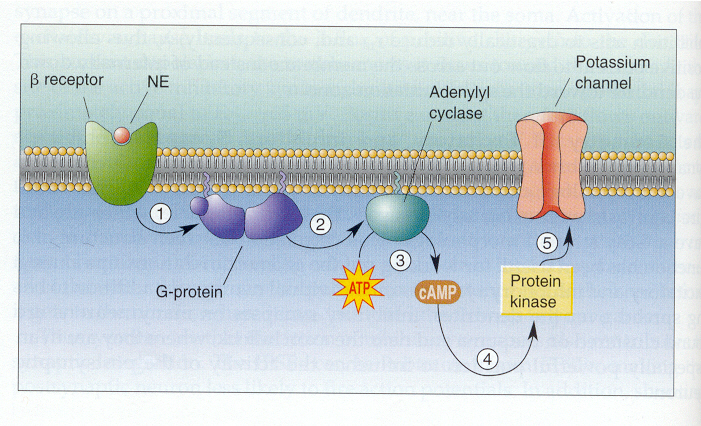
Figure 5.21 Modulation by the NE b receptor. (1) The binding of NE to the receptor activates a G-protein in the membrane. (2) The G-protein activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase. (3) Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into the second messenger cAMP. (4) cAMP activates a protein kinase. (5) cAMP kinase causes a potassium channel to close by attaching a phosphate group to it.
NE = norepinephrine