Cognitive Science 320
![]()
The Circuitry of the central pattern generator that controls the pyloric regions of the stomach in the crab. AB is an interneuron, the other cells are motor neurons. All of the chemical synapses make up the circuit are inhibitory (filled circles); the synapses between the AB, PD, and VD neurons are electrical (resistor symbols). The function of the AB is an interneuron, PD is a dilator, LP is a constrictor, VD is a dilator, IC = ?, and PY is a constrictor. (Information taken from Neurons and Networks An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, 2nd edition by John Dowling.)
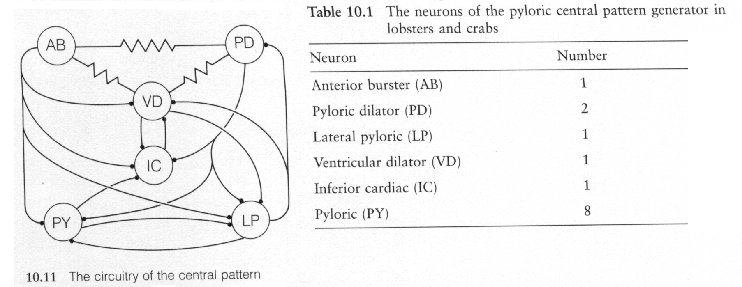
Not all of the synapses have equal strengths. For example, the electrical coupling between the AB and PD neurons is very strong, whereas the electrical coupling between the AB and VD neurons and the PD and VD neurons is usually weak.
Some features of the circuitry are:
the AB neuron is spontaneously active, firing bursts of impulses rhythmically.
the strong electrical coupling of the AB neuron to the PD neurons means that the AB and PD cells depolarize synchronously and fire in phase.
The AB and PD neurons inhibit the LP and PY constrictor neurons, which consequently fire out of phase with the AB and PD neurons.
Because reciprocal inhibitory synapses are located between the LP and PY neurons, these cells are also out of phase with one another.
There are multiple neurotransmitters involved which regulate the strength of synaptic connections: dopamine, octopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine, histamine, proctolin, and other neuropeptides.
Neuromodulators can redefine the circuitry of a central pattern generator in a variety of ways.
they may switch a circuit from one configuration to another so that quite different behaviors are mediated by the circuit
they may fine tune the circuit and subtly alter its output in response to slightly different environmental conditions.
changes in the circuit induced by neuromodulatory substances may be relatively short term (on the order of seconds) or they may last for substantial periods of time (minutes or more).
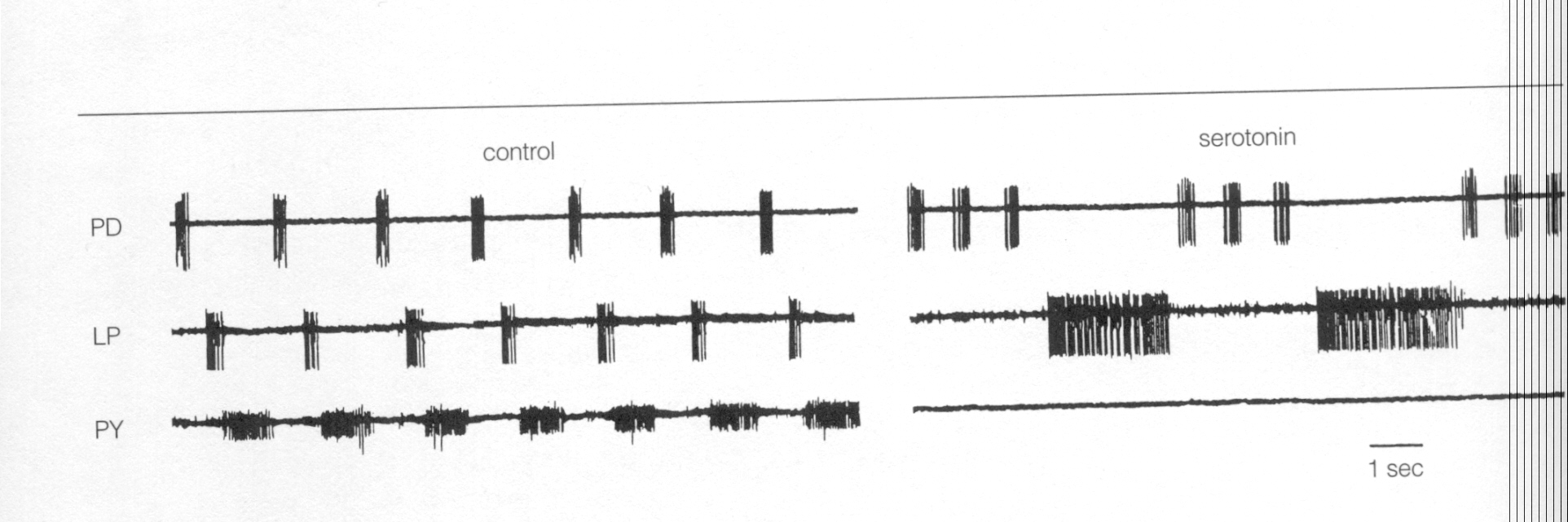
The above figure shows the effects of serotonin (at the right) on three of the neurons in the pyloric central pattern generator. Following the application of serotonin, the alternating bursting of activity between the PD and LP neurons is replaced by a pattern in which three PD bursts are interspersed between one long LP burst of activity. Furthermore, the PY neuron ceases to fire when serotonin is present.
The three following figures show the major functional synaptic pathways in the pyloric central pattern generator following the application of dopamine, octopamine, and serotonin, respectively, to the stomatogastric ganglion. These agents increase the strength of some synaptic interactions, weaken others, and leave some unchanged.
|
dopamine |
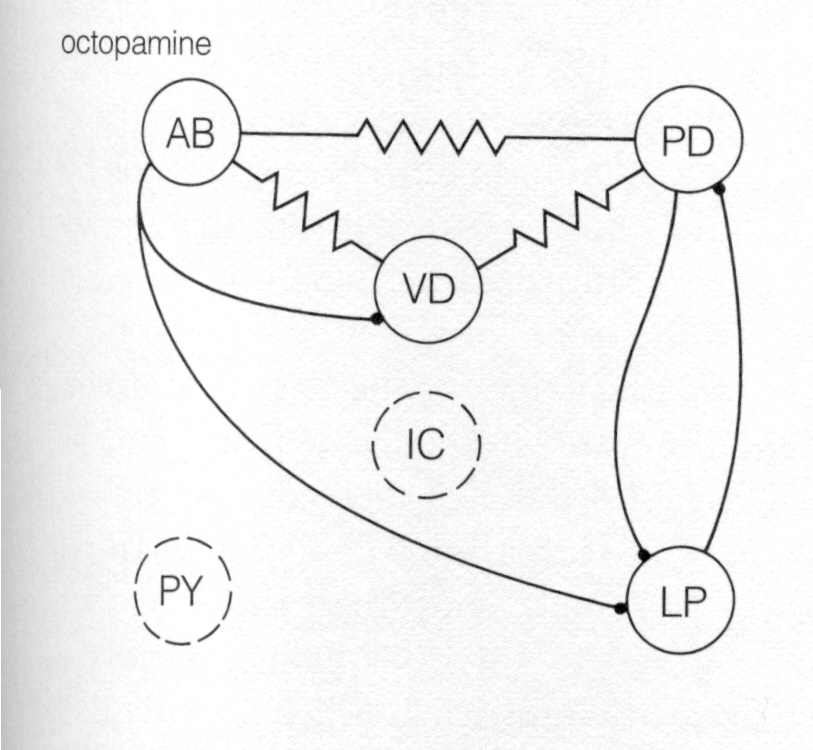
octopamine |
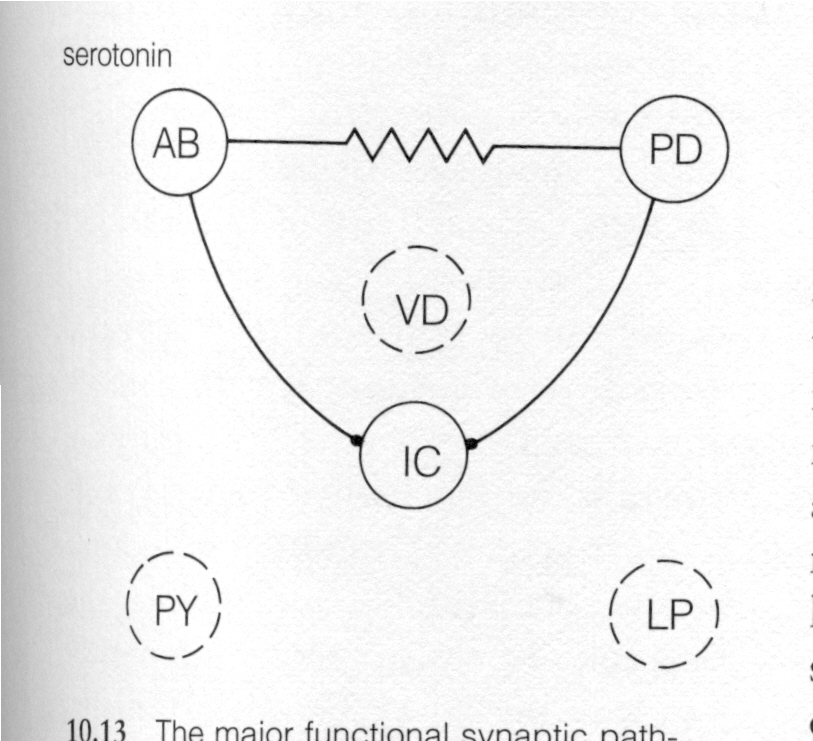
serotonin |