Cognitive Science 320
![]()
Electrical Synapses in Aplysia, a marine snail (picture of Aplysia): A group of electrically coupled motor neurons firing together is an effective system for producing instantaneous, all-or-none behaviors. Such a system is used by the marine snail Aplysia to release a protective cloud of ink when the animal is perturbed.
B. Sensory neurons from the tail ganglion synapse on three motor neurons that project to the ink gland. The black rectangular box at the right represents the ink gland. The motor neurons are interconnected by means of electrical synapses.
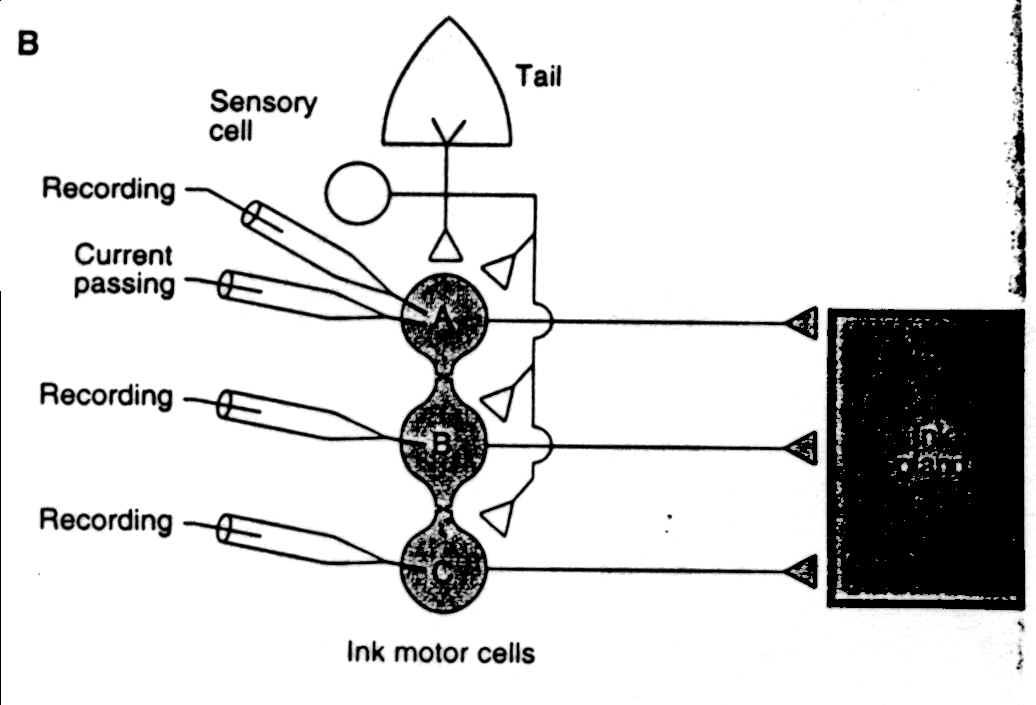
C. A train of stimuli applied to the tail produces a synchronized discharge in all three motor neurons.
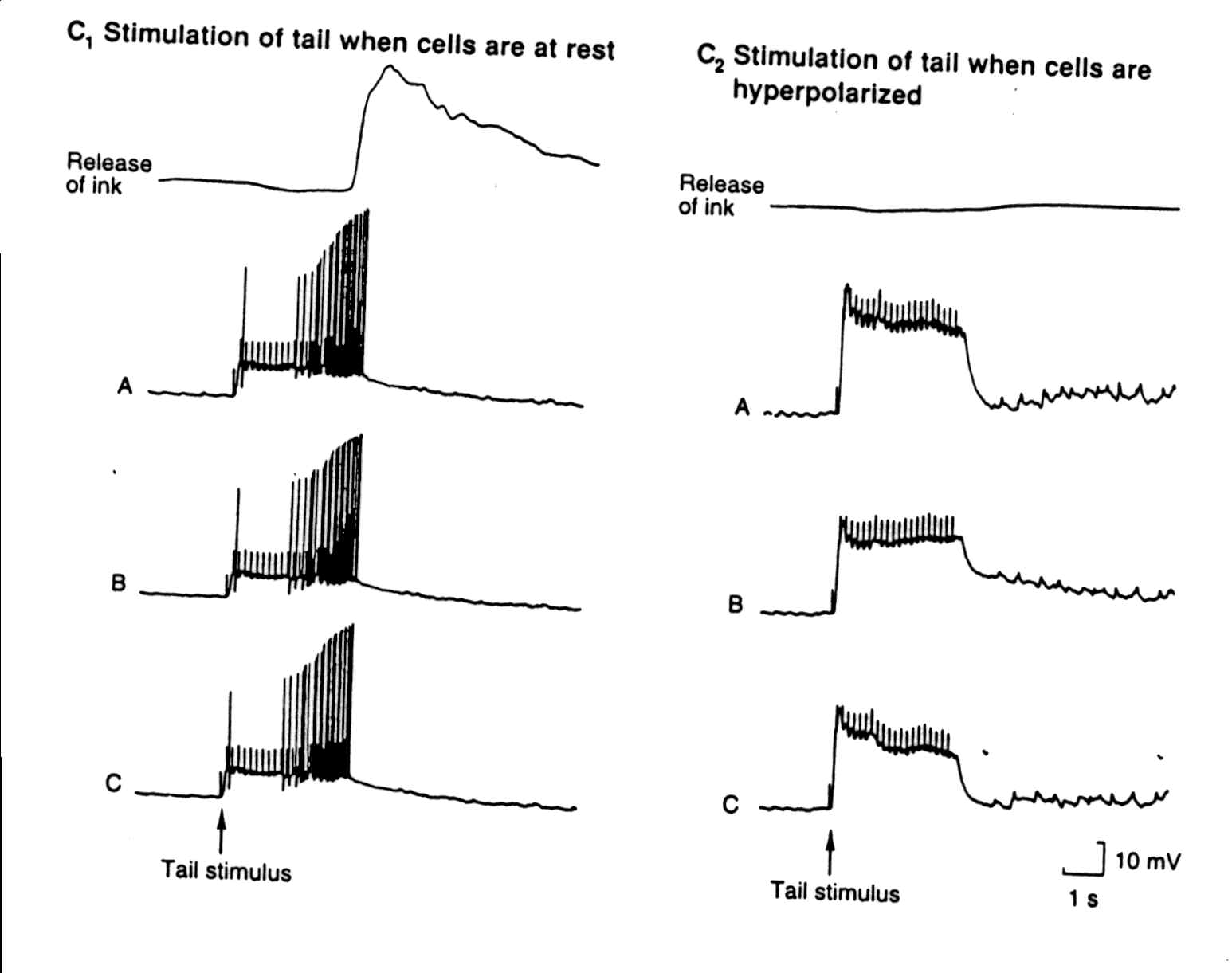
C1. When the cells are at rest the stimulus triggers a train of identical action potentials in all three cells. This synchronous activity in the motor neurons results in the release of ink.
C2. When the cells are hyperpolarized, the stimulus cannot trigger action potentials, because the cells are too far from their threshold level. Under these conditions, the inking response is blocked.
(Adapted from Carew and Kandel, 1976)