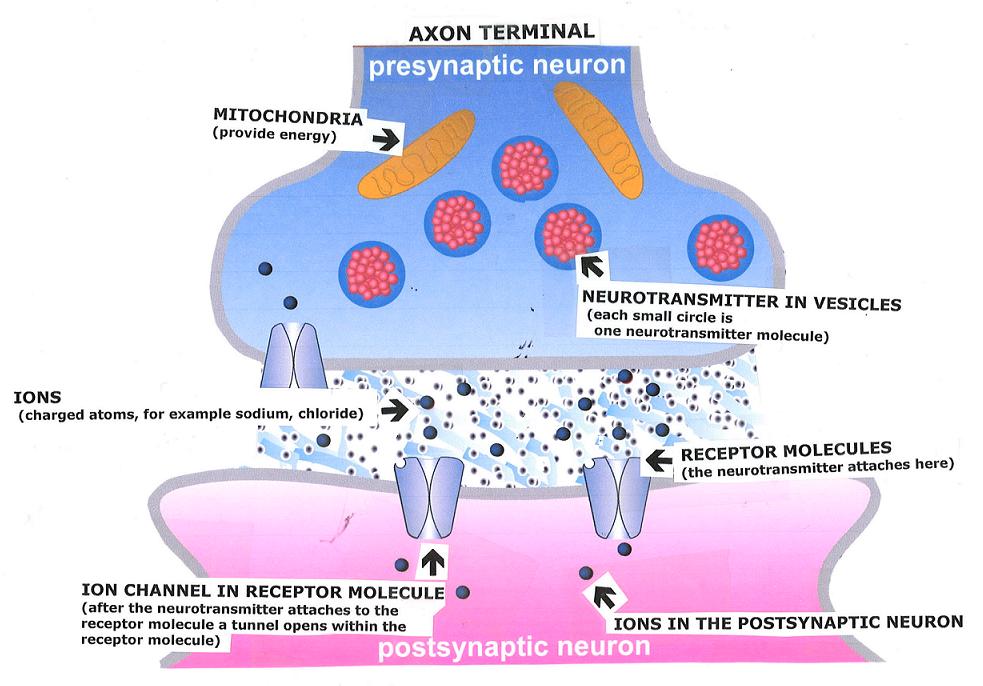
Steps in the functioning of a synapse
1. Electrical charge (an action potential) moves into the
presynaptic neuron's axon terminal.
2. The electrical charge causes calcium channels in the
membrane to open - this allows calcium ions to move into the presynaptic
neuron at the axon terminal.
3. The calcium ions attach to and modify proteins on the
outside of the synaptic vesicles (which contain the neurotransmitter
molecules).
4. The calcium-activated synaptic vesicles fuse with
the membrane of the axon terminal (presynaptic neuron) at special docking
sites and release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft (the space
between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons).
a. some of those neurotransmitter molecules attach to receptor molecules on the surface of the postsynaptic neuron.
b. some of those neurotransmitter molecules are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron by reuptake.
6. When neurotransmitter molecules attach to receptor molecules on the surface of the postsynaptic neuron, the receptor molecule opens a passageway, called an ion channel.
7. If this is a neurotransmitter that excites the postsynaptic neuron, positively charged ions (usually sodium, Na+) enter through the receptor's ion channel.
8. If this is a neurotransmitter that inhibits the postsynaptic neuron, negatively charged ions (usually chloride, Cl-) enter through the receptor's ion channel.