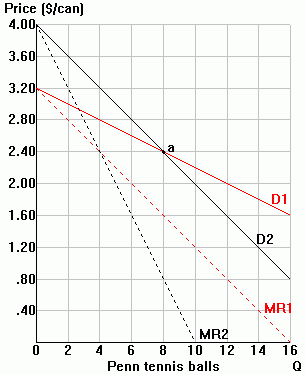
 The diagram to the right
depicts Penn's sales of tennis balls. Penn currently produces and prices at
point a:
The diagram to the right
depicts Penn's sales of tennis balls. Penn currently produces and prices at
point a:Output = 8
Price = 2.40
|
Friday, April 12, 2013 |
Oligopoly conduct: Example 2 Kinked demand theory
 The diagram to the right
depicts Penn's sales of tennis balls. Penn currently produces and prices at
point a:
The diagram to the right
depicts Penn's sales of tennis balls. Penn currently produces and prices at
point a:
Output = 8
Price = 2.40
Penn realizes that its demand is (select "more" or "less") ________ elastic if it changes its price and its rivals do
not change their price at the same time. As a result, choosing between D1 and D2
in the diagram to the right, Penn's demand
= ______ if only Penn changes its price
= ______ if Penn and its rivals change their price together
Suppose that Penn assumes:
a. if it raises its price, its rivals will NOT change their price, and
b. if it lowers its price, its rivals WILL also lower their price.
1. Indicate Penn's perceived demand curve if Penn raises its price. Indicate also Penn's corresponding marginal revenue curve.
2. Indicate Penn's perceived demand curve if Penn lowers its price. Again, indicate Penn's corresponding marginal revenue curve.
3. For future reference, link together your two marginal revenue segments.
4. Complete the following table of Penn's profit-maximizing quantity and expected price for each of the following constant cost marginal cost curves:
| Case | Marginal cost |
Penn's profit-maximizing... | |
| Quantity | Price | ||
| 1 | $.80 | 8 | $2.40 |
| 2 | 1.20 | ||
| 3 | 1.60 | ||
| 4 | 2.00 | ||
| 5 | 0.40 | ||
5. Note: D1 and D2 both cross at point a, Penn's current output and price combination. Is it just coincidence that MR1 and MR2 also cross at Penn's current price of $2.40? Why or why not?