|
Friday, March 29, 2013 |

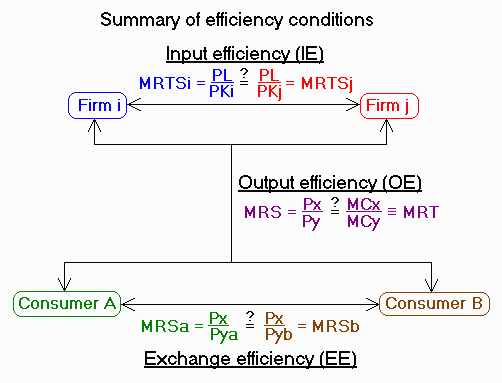
Testing for economic efficiency
Consider 2 consumers (A and B), 2 goods (x and y), 2 producers (i and j) and 2 inputs (L and K).
A. Exchange efficiency (EE): distributing output to maximize uitlity
Do all consumers have the same marginal rates of substitution (MRS)
between goods?
The market test: MRS will be equated for all consumers if they all face
the same set of market-clearing prices for equivalent products.
Ex: MRS will be the same for A
and B if they both pay Px/Py and can buy as much as they want.
B. Input efficiency (IE): choosing production techniques to minimize costs
Do all producers have the same marginal rates of technical substitution
(MRTS) between inputs?
The market test: MRTS will be equated for all producers if they all
face the same set of market-clearing prices for equivalent inputs.
Ex: MRTS will be the same for i
and j if they both pay PL/PK and can buy as much as they want.
C. Output efficiency (OE): allocating resources to their highest valued uses
Do the marginal rates of substitution (MRS) between goods equal the
opportunity costs of those goods (MRT)?
The market test: MRS will equal MRT if market-clearing output prices
equal marginal costs (MC).
Ex: MRS will equal MRT if Px/Py
equals MCx/MCy and everyone can buy or sell as much as they want.
Sample questions:
1. Label each of the following as "efficient" (e) or
"inefficient" (i). Inefficiency always means that output efficiency (OE)
is violated. For the cases that you classify as inefficient, indicate whether
you think that exchange efficiency (EE) or input efficiency (IE) also fails to
hold.
i:IE Example: Water prices are
lower for rural farmers than for urban industrial firms.
_____ a. Disneyland offers special deals that result in lower prices
for local residents than for out-of-town tourists.
_____ b. Minimum wage laws cover unskilled workers in manufacturing but
not unskilled workers in agriculture.
_____ c. Until World War II, Alcoa was the only aluminum foil producer
in the U.S.
_____ d. Long distance phone rates are higher during the day (when
congested phone lines raise the costs of service) than they are at night.
_____ e. The Post Office charges the same price for all first class
mail regardless of the distance the letter is sent.
2. True or false (T/F):
_____ a. A tax on shipbuilding would reduce efficiency, but a subsidy
for shipbuilding would raise efficiency.
_____ b. A price ceiling on natural gas will cause output inefficiency,
but using ration coupons to distribute the available natural gas will tend to ensure
exchange efficiency unless the ration coupons are non-marketable.